274. H-Index
Given an array of integers citations where{" "}
citations[i] is the number of citations a researcher received
for their{" "}
ith
{" "}
paper, return compute the researcher's h
-index.
According to the{" "}
definition of h-index on Wikipedia
: A scientist has an index h if h of their{" "}
n papers have at least h citations each, and the
other n − h papers have no more than h citations
each.
If there are several possible values for h, the maximum one is
taken as the h
-index.
Example 1:
Input: citations = [3,0,6,1,5]{"\n"}
Output: 3{"\n"}
Explanation: [3,0,6,1,5] means the researcher has 5 papers
in total and each of them had received 3, 0, 6, 1, 5 citations respectively.
{"\n"}Since the researcher has 3 papers with at least 3 citations each and
the remaining two with no more than 3 citations each, their h-index is 3.
{"\n"}
Example 2:
Input: citations = [1,3,1]{"\n"}
Output: 1{"\n"}
Constraints:
-
n == citations.length -
1 <= n <= 5000 -
0 <= citations[i] <= 1000
Solution
Naive Solution
We can try all possible values of h from 0to n. For each h, loop through citations to see if h is a possible h-index, using the condition we are given:
A scientist has an index
hifhof theirnpapers have at least h citations each, and the othern-hpapers have no more thanhcitations each.
The answer is the highest h for which this is true.
This takes time because for each of the n+1 possible h values, we have to loop through n citations.
Binary Search Solution
Create a function hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations with a parameter h to check if there are at least h papers with >= h citations. When hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(x) is true, hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(x-1) is also true. This means that hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations is a monotonic function, so we can binary search for the highest h for which it return true. This h is our h-index.
Time Complexity
Each call to hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations checks all papers, taking .
Binary searching the range takes .
Multiplying these together, we take .
Space Complexity
citations is passed by reference, so we aren't allocating any memory for it. We allocate a constant amount of memory for a couple of variables, so the space complexity is .
C++ Solution
1class Solution {
2public:
3 bool hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(int h, vector<int>& citations) {
4 int count = 0;
5 for (int cite_count : citations) {
6 if (cite_count >= h)
7 count++;
8 }
9 return count >= h;
10 }
11 int hIndex(vector<int>& citations) {
12 int low = 0, high = citations.size();
13 while (low <= high) {
14 int mid = (low + high) / 2;
15 if (hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(mid, citations))
16 low = mid + 1;
17 else
18 high = mid - 1;
19 }
20 return high;
21 }
22};
Java Solution
1class Solution {
2 static boolean hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(int h, int[] citations) {
3 int count = 0;
4 for (int cite_count : citations) {
5 if (cite_count >= h)
6 count++;
7 }
8 return count >= h;
9 }
10 public int hIndex(int[] citations) {
11 int low = 0, high = citations.length;
12 while (low <= high) {
13 int mid = (low + high) / 2;
14 if (hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(mid, citations))
15 low = mid + 1;
16 else
17 high = mid - 1;
18 }
19 return high;
20 }
21}
Python Solution
1class Solution: 2 def hIndex(self, citations: List[int]) -> int: 3 4 def hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(h, citations): 5 return sum(cite_count >= h for cite_count in citations) >= h 6 7 low = 0 8 high = len(citations) 9 while low <= high: 10 mid = (low + high) // 2; 11 if hasAtLeastHPapersWithHCitations(mid, citations): 12 low = mid + 1; 13 else: 14 high = mid - 1; 15 return high
Sort and Loop Solution
First we sort the papers by decreasing # of citations. Imagine a histogram where each bar represents a paper and its height is the # of citations it has.
<img src={require('@site/static/img/274/1.png').default} style={{ height: 450 }}/>
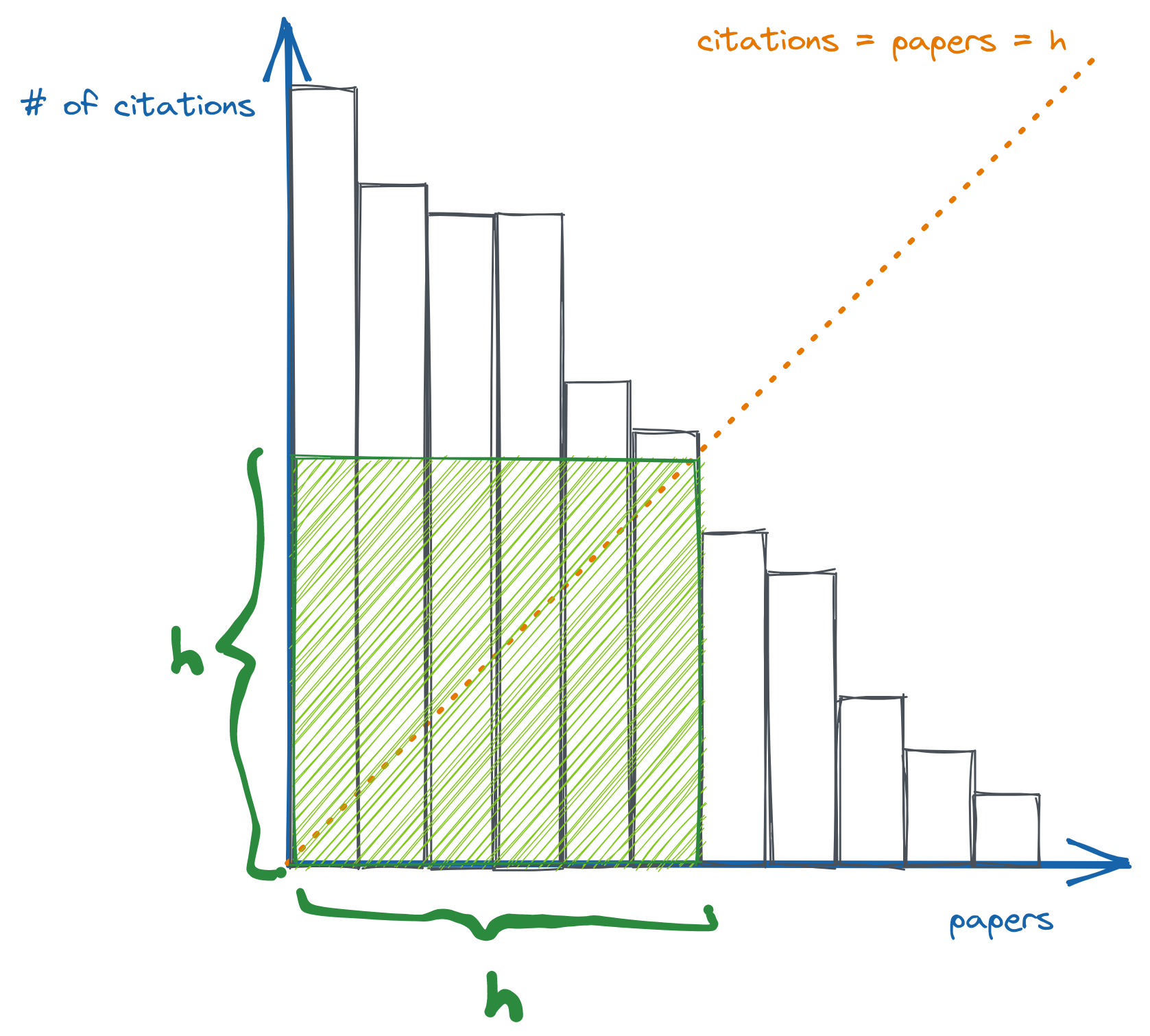
If the h-index were h, we'd need exactly h bars with height as least h. That is to say, we'd need the green square covered by bars. To find the h index, first set h = 0. Then keep increasing h by 1 as long as the next tallest bar is >= h+1. When we can no longer increase h, we have our answer.
In the diagram above, if we continued to increase h, the next added bar would not be tall enough for the new h.
Time Complexity
Sorting is . Looping h is . So the time complexity is .
Space Complexity
The only memory we allocate is the integer h, so the space complexity is .
C++ Solution
1class Solution {
2public:
3 int hIndex(vector<int>& citations) {
4 sort(citations.rbegin(), citations.rend());
5 int h = 0;
6 while (h < citations.size() and citations[h] >= h+1) {
7 h++;
8 }
9 return h;
10 }
11};
Java Solution
1class Solution {
2 public int hIndex(int[] citations) {
3 // Sorting an int[] in reverse in Java is annoying
4 // We first sort normally then reverse the array
5 Arrays.sort(citations);
6 for (int i = 0; i < citations.length/2; i++) {
7 int tmp = citations[i];
8 citations[i] = citations[citations.length-1-i];
9 citations[citations.length-1-i] = tmp;
10 }
11
12 int h = 0;
13 while (h < citations.length && citations[h] >= h+1) {
14 h++;
15 }
16 return h;
17 }
18}
Python Solution
1class Solution: 2 def hIndex(self, citations: List[int]) -> int: 3 citations.sort(reverse=True) 4 h = 0 5 while h < len(citations) and citations[h] >= h+1: 6 h += 1 7 return h
Given a sorted array of integers and an integer called target, find the element that
equals to the target and return its index. Select the correct code that fills the
___ in the given code snippet.
1def binary_search(arr, target):
2 left, right = 0, len(arr) - 1
3 while left ___ right:
4 mid = (left + right) // 2
5 if arr[mid] == target:
6 return mid
7 if arr[mid] < target:
8 ___ = mid + 1
9 else:
10 ___ = mid - 1
11 return -1
121public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
2 int left = 0;
3 int right = arr.length - 1;
4
5 while (left ___ right) {
6 int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
7 if (arr[mid] == target) return mid;
8 if (arr[mid] < target) {
9 ___ = mid + 1;
10 } else {
11 ___ = mid - 1;
12 }
13 }
14 return -1;
15}
161function binarySearch(arr, target) {
2 let left = 0;
3 let right = arr.length - 1;
4
5 while (left ___ right) {
6 let mid = left + Math.trunc((right - left) / 2);
7 if (arr[mid] == target) return mid;
8 if (arr[mid] < target) {
9 ___ = mid + 1;
10 } else {
11 ___ = mid - 1;
12 }
13 }
14 return -1;
15}
16What's the output of running the following function using the following tree as input?

1def serialize(root):
2 res = []
3 def dfs(root):
4 if not root:
5 res.append('x')
6 return
7 res.append(root.val)
8 dfs(root.left)
9 dfs(root.right)
10 dfs(root)
11 return ' '.join(res)
121import java.util.StringJoiner;
2
3public static String serialize(Node root) {
4 StringJoiner res = new StringJoiner(" ");
5 serializeDFS(root, res);
6 return res.toString();
7}
8
9private static void serializeDFS(Node root, StringJoiner result) {
10 if (root == null) {
11 result.add("x");
12 return;
13 }
14 result.add(Integer.toString(root.val));
15 serializeDFS(root.left, result);
16 serializeDFS(root.right, result);
17}
181function serialize(root) {
2 let res = [];
3 serialize_dfs(root, res);
4 return res.join(" ");
5}
6
7function serialize_dfs(root, res) {
8 if (!root) {
9 res.push("x");
10 return;
11 }
12 res.push(root.val);
13 serialize_dfs(root.left, res);
14 serialize_dfs(root.right, res);
15}
16Solution Implementation
In a binary min heap, the minimum element can be found in:
How does quick sort divide the problem into subproblems?
Recommended Readings
Top Patterns to Conquer the Technical Coding Interview Should the written word bore you fear not A delightful video alternative awaits iframe width 560 height 315 src https www youtube com embed LW8Io6IPYHw title YouTube video player frameborder 0 allow accelerometer autoplay clipboard write encrypted media gyroscope picture in picture
Recursion Recursion is one of the most important concepts in computer science Simply speaking recursion is the process of a function calling itself Using a real life analogy imagine a scenario where you invite your friends to lunch https algomonster s3 us east 2 amazonaws com recursion jpg You first
Runtime Overview When learning about algorithms and data structures you'll frequently encounter the term time complexity This concept is fundamental in computer science and offers insights into how long an algorithm takes to complete given a certain input size What is Time Complexity Time complexity represents the amount of time
Got a question? Ask the Teaching Assistant anything you don't understand.
Still not clear? Ask in the Forum, Discord or Submit the part you don't understand to our editors.